Our mission is to ensure the generation of accurate and precise findings.
Please enter subscribe form shortcode
Please enter instagram feed shortcode
Pharmacodynamics
Piperacillin sodium exerts bactericidal activity by inhibiting septum formation and cell wall synthesis of susceptible bacteria. In vitro, piperacillin is active against a variety of gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Tazobactam sodium has little clinically relevant in vitro activity against bacteria due to its reduced affinity to penicillin-binding proteins. It is, however, a beta-lactamase inhibitor of the Richmond-Sykes class III (Bush class 2b & 2b’) penicillinases and cephalosporinases. It varies in its ability to inhibit class IIA and IV (2a & 4) penicillinases. Tazobactam does not induce chromosomally-mediated beta-lactamases at tazobactam concentrations achieved with the recommended dosage regimen.
Piperacillin/tazobactam has been shown to be active against most strains of the following microorganisms both in vitro and in clinical infections.
Aerobic and facultative Gram-positive microorganisms: Staphylococcus aureus (excluding methicillin and oxacillin-resistant isolates)
Aerobic and facultative Gram-negative microorganisms:
Gram-negative anaerobes:
Bacteroides fragilis group (B. fragilis, B. ovatus, B. thetaiotaomicron, and B. vulgatus)
Pharmacokinetics
Peak plasma concentrations of piperacillin and tazobactam are attained immediately after completion of an intravenous infusion of piperacillin/ tazobactam. Piperacillin plasma concentrations, following a 30-minute infusion of piperacillin/tazobactam, were similar to those attained when equivalent doses of piperacillin were administered alone, with mean peak plasma concentrations of approximately 134 and 298 μg/ml for the 2.25 g and 4.5 g piperacillin/tazobactam doses, respectively. The corresponding mean peak plasma concentrations of tazobactam were 15 and 34 μg/ml, respectively.
Piperacillin is metabolized to a minor microbiologically active desethyl metabolite.
Tazobactam is metabolized to a single metabolite that lacks pharmacological and antibacterial activities. Both piperacillin and tazobactam are eliminated via the kidney by glomerular filtration and tubular secretion. Piperacillin is excreted rapidly as unchanged drug with 68% of the administered dose excreted in the urine. Tazobactam and its metabolite are eliminated primarily by renal excretion with 80% of the administered dose excreted as unchanged drug and the remainder as the single metabolite. Piperacillin, tazobactam and desethyl piperacillin are also secreted into the bile. Both piperacillin and tazobactam are approximately 30% bound to plasma proteins. The protein binding of either piperacillin or tazobactam is unaffected by the presence of the other compound. Protein binding of the tazobactam metabolite is negligible.
Piperacillin and tazobactam are widely distributed into tissues and body fluids including intestinal mucosa, gallbladder, lung, female reproductive tissues (uterus, ovary, and fallopian tube), interstitial fluid, and bile. Mean tissue concentrations are generally 50% to 100% of those in plasma. Distribution of piperacillin and tazobactam into cerebrospinal fluid is low in subjects with non-inflamed meninges, as with other penicillins.
TAZSUP 4.5 Injection is indicated for the treatment of patients with moderate to severe infections caused by piperacillinresistant, piperacillin/tazobactam susceptible, beta -lactamase producing strains of the designated microorganisms in the specified conditions listed below:
Appendicitis (complicated by rupture or abscess) and peritonitis caused by piperacillin-resistant, beta-lactamase producing strains of Escherichia coli or the following members of the Bacteroides fragilis group: B. fragilis, B. ovatus, B. thetaiotaomicron, or B. vulgatus.
Uncomplicated and complicated skin and skin structure infections, including cellulitis, cutaneous abscesses and ischemic/diabetic foot infections caused by piperacillin-resistant, beta-lactamase producing strains of Staphylococcus aureus.
Postpartum endometritis or pelvic inflammatory disease caused by piperacillin-resistant, beta-lactamase producing strains of Escherichia coli.
Community-acquired pneumonia (moderate severity only) caused by piperacillin-resistant, beta-lactamase producing strains of Haemophilus influenzae.
Nosocomial pneumonia (moderate to severe) caused by piperacillin-resistant, betalactamase producing strains of Staphylococcus aureus and by piperacillin/tazobactam susceptible.
TAZSUP 4.5 should be administered by intravenous infusion over 30 minutes.
Adults: The usual total daily dose of TAZSUP 4.5 is every six hours or as directed by the Physician.
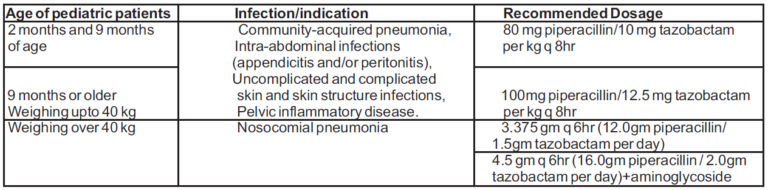
Pediatrics
TAZSUP 4.5 can be administered in pediatric patients from 2 months of age. The dosage and the indications in pediatric patients with normal renal function are as follows:
Duration of Therapy
The usual duration of TAZSUP 4.5 treatment is from seven to ten days. However, the recommended duration of TAZSUP 4.5 treatment of nosocomial pneumonia is 7 to 14 days. In all conditions, the duration of therapy should be guided by the severity of the infection and the patient’s clinical and bacteriological progress.
Pediatrics:
There are no dosage recommendations for piperacillin/tazobactam in pediatric patients with impaired renal function.
TAZSUP 4.5 is contraindicated in patients with a history of allergic reactions to any of the penicillins, cephalosporins, or beta-lactamase inhibitors.
Pregnancy
Reproduction studies performed in animals have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility due to piperacillin/tazobactam administered up to a dose which is similar to the maximum recommended human daily dose based on body-surface area (mg/m 2).
Lactation
Piperacillin is excreted in low concentrations in human milk; tazobactam concentrations in human milk have not been studied. Caution should be exercised when TAZSUP 4.5 is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy in pediatric patients less than 2 months of age have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Patients over 65 years are not an increased risk of developing adverse effects solely because of age. However, dosage should be adjusted in the presence of renal insufficiency.
There have been postmarketing reports of overdose with piperacillin/tazobactam. The majority of those events experienced, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhoea, have also been reported with the usual recommended dosages. Patients may experience neuromuscular excitability or convulsions if higher than recommended doses are given intravenously (particularly in the presence of renal failure).
Treatment should be supportive and symptomatic according the patient’s clinical presentation. Excessive serum concentrations of either piperacillin or tazobactam may be reduced by haemodialysis. Following a single 3.375 g dose of piperacillin/tazobactam, the percentage of the piperacillin and tazobactam dose removed by haemodialysis was approximately 31% and 39%, respectively.
Constitute using 20 ml Sterile Water for Injections IP. The constituted solution should be used immediately after preparation.
WhatsApp us
