Our mission is to ensure the generation of accurate and precise findings.
Please enter subscribe form shortcode
Please enter instagram feed shortcode
Powder for solution for injection or infusion.
Meropenem injection is indicated for the treatment of pneumonia, nonocomial pneumonia, UTI, intra-abdominal infection, gynaecological infection, skin & soft tissue infection, meningitis, septicaemia & empiric treatment of presumed infection in adult patients with febrile neutropenia. For treatment, in children, of the following infections caused by single or multiple bacteria sensitive to Meropenem: Pneumonias and nosocomial pneumonias, urinary tract infections, intra-abdominal infections, Gynaecological infections.
Posology
The dose of meropenem administered and the duration of treatment should take into account the type of infection to be treated, including its
severity, and the clinical response.
Paediatric population:
Children under 3 months of age: The safety and efficacy of meropenem in children under 3 months of age have not been established and the optimal dose regimen has not been identified. However, limited pharmacokinetic data suggest that 20 mg/kg every 8 hours may be an appropriate regimen.
Paediatric patients ≥ 3 months of age: The recommended dose regimen of meropenem is 10 – 40 mg/kg depending upon the severity of infection and to be administered every 8 hours.
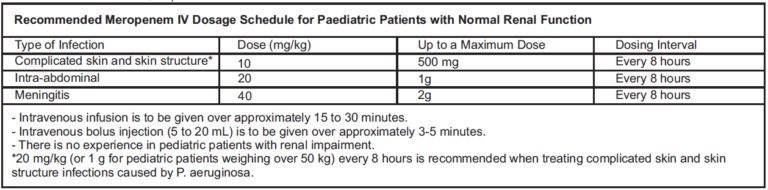
Children over 50 kg body weight: The adult dose should be administered.
There is no experience in children with renal impairment.
Adults and Adolescents: Meropenem is usually given by intravenous infusion over approximately 15 to 30 minutes. Alternatively, doses up to 1g can be given as an intravenous bolus injection over approximately 5 minutes. There are limited safety data available to support the administration of a 2 g dose in adults as an intravenous bolus injection.
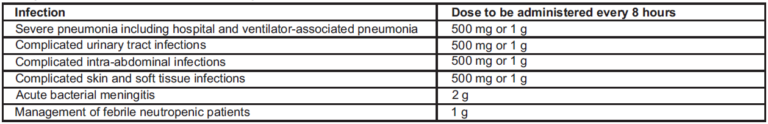
A maximum dose of up to 2 g three times daily in adults and adolescents and a dose of up to 40 mg/kg three times daily in children may be particularly appropriate when treating some types of infections, such as infections due to less susceptible bacterial species (e.g. Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter spp.), or very severe infections. Additional considerations for dosing are needed when treating patients with renal insufficiency.
Renal impairment: The dose for adults and adolescents should be adjusted when creatinine clearance is less than 51 ml/min, as shown below. There are limited data to support the application of these dose adjustments for a unit dose of 2 g.
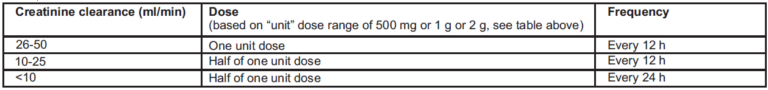
Meropenem is cleared by the haemodialysis and haemofiltration. The required dose should be administered after completion of the haemodialysis cycle.
There are no established dose recommendations for patients receiving peritoneal dialysis.
Hepatic impairment: No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with hepatic impairment
Dose in elderly patients: No dose adjustment is required for the elderly with normal renal function or creatinine clearance values above 50ml/min.
Method of administration: For Intravenous (IV) use only.
Meropenem is usually given by intravenous infusion over approximately 15 to 30 minutes. Alternatively, meropenem doses of up to 20 mg/kg may be given as an intravenous bolus over approximately 5 minutes. There are limited safety data available to support the administration of a 40 mg/kg dose in children as an intravenous bolus injection.
Intravenous Bolus Administration: Meropenem IV injection vials re-constituted with sterile Water for Injection for bolus administration (up to 50mg/mL of Meropenem IV) may be stored for up to 3 hours at up to 25°C.
Intravenous Infusion Administration: Solutions prepared for infusion (Meropenem IV concentrations ranging from 1 mg/mL to 20 mg/mL) reconstituted with Sodium Chloride Injection 0.9% may be stored for 1 hour at up to 25°C.
Solutions prepared for infusion (Meropenem IV concentrations ranging from 1 mg/mL to 20 mg/mL) re-constituted with Dextrose Injection 5% should be used immediately.
Contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the active substance or any of the excipients.
– Hypersensitivity to any other carbapenem antibacterial agent.
– Severe hypersensitivity (e.g. anaphylactic reaction, severe skin reaction) to any other type of beta-lactam antibacterial agent (e.g. penicillins or
cephalosporins).
The selection of meropenem to treat an individual patient should take into account the appropriateness of using a carbapenem antibacterial agent based on factors such as severity of the infection, the prevalence of resistance to other suitable antibacterial agents and the risk of selecting for carbapenem-resistant bacteria.
Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter spp. Resistance
Resistance to penems of Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter spp. varies across the European Union. Prescribers are advised to take into account the local prevalence of resistance in these bacteria to penems.
Hypersensitivity reactions
As with all beta-lactam antibiotics, serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity reactions have been reported. Patients who have a history of hypersensitivity to carbapenems, penicillins or other beta-lactam antibiotics may also be hypersensitive to meropenem. Before initiating therapy with meropenem, careful inquiry should be made concerning previous hypersensitivity reactions to beta-lactam antibiotics. If a severe allergic reaction occurs, the medicinal product should be discontinued and appropriate measures taken.
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR), such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), erythema multiforme (EM) and acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) have been reported in patients receiving meropenem. If signs and symptoms suggestive of these reactions appear, meropenem should be withdrawn immediately and an alternative treatment should be considered.
Antibiotic-associated colitis
Antibiotic-associated colitis and pseudomembranous colitis have been reported with nearly all anti-bacterial agents, including meropenem, and may range in severity from mild to life threatening. Therefore, it is important to consider this diagnosis in patients who present with diarrhoea during or subsequent to the administration of meropenem. Discontinuation of therapy with meropenem and the administration of specific treatment for Clostridium difficile should be considered. Medicinal products that inhibit peristalsis should not be given.
Seizures
Seizures have infrequently been reported during treatment with carbapenems, including meropenem.
Hepatic function monitoring
Hepatic function should be closely monitored during treatment with meropenem due to the risk of hepatic toxicity (hepatic dysfunction with cholestasis and cytolysis).
Use in patients with liver disease: patients with pre-existing liver disorders should have liver function monitored during treatment with meropenem. There is no dose adjustment necessary.
Direct antiglobulin test (Coombs test) seroconversion
A positive direct or indirect Coombs test may develop during treatment with meropenem.
Concomitant use with valproic acid/sodium valproate/valpromide
The concomitant use of meropenem and valproic acid/sodium valproate/valpromide is not recommended.
Meropenem contains sodium
No specific medicinal product interaction studies other than probenecid were conducted.
Probenecid
Probenecid competes with meropenem for active tubular secretion and thus inhibits the renal excretion of meropenem with the effect of increasing the elimination half-life and plasma concentration of meropenem. Caution is required if probenecid is co-administered with meropenem.
The potential effect of meropenem on the protein binding of other medicinal products or metabolism has not been studied. However, the protein binding is so low that no interactions with other compounds would be expected on the basis of this mechanism.
Valproic acid
Decreases in blood levels of valproic acid have been reported when it is co-administered with carbapenem agents resulting in a 60-100 % decrease in valproic acid levels in about two days. Due to the rapid onset and the extent of the decrease, co-administration of valproic acid/sodium valproate/valpromide with carbapenem agents is not considered to be manageable and therefore should be avoided.
Oral anti-coagulants
Simultaneous administration of antibiotics with warfarin may augment its anti-coagulant effects. There have been many reports of increases in the anti-coagulant effects of orally administered anti-coagulant agents, including warfarin in patients who are concomitantly receiving antibacterial agents. The risk may vary with the underlying infection, age and general status of the patient so that the contribution of the antibiotic to the increase in INR (international normalised ratio) is difficult to assess. It is recommended that the INR should be monitored frequently during and shortly after co-administration of antibiotics with an oral anti-coagulant agent.
Pregnancy
There are no or limited amount of data from the use of meropenem in pregnant women. Animal studies do not indicate direct or indirect harmful effects with respect to reproductive toxicity. As a precautionary measure, it is preferable to avoid the use of meropenem during pregnancy.
Lactation
Small amounts of meropenem have been reported to be excreted in human milk. Meropenem should not be used in breast-feeding women unless the potential benefit for the mother justifies the potential risk to the baby.
No studies on the effect on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed. However, when driving or operating machines, it should be taken into account that headache, paraesthesia and convulsions have been reported for meropenem.
Hypokalemia
Hypokalemia as an Adverse drug reaction has been reported with the use of Meropenem.
In a review of 4,872 patients with 5,026 meropenem treatment exposures, meropenem-related adverse reactions most frequently reported were diarrhoea (2.3 %), rash (1.4 %), nausea/vomiting (1.4 %) and injection site inflammation (1.1 %). The most commonly reported meropenemrelated laboratory adverse events were thrombocytosis (1.6 %) and increased hepatic enzymes (1.5-4.3 %).
Risk of adverse reactions: Below all adverse reactions are listed by system organ class and frequency: very common (≥ 1/10); common (≥ 1/100 to <1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 to <1/100); rare (≥ 1/10,000 to <1/1,000); very rare (< 1/10,000), not known (cannot be estimated from the available data). Within each frequency grouping, undesirable effects are presented in order of decreasing seriousness.
Infections and infestations: Uncommon: oral and vaginal candidiasis.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Common: thrombocythaemia. Uncommon: eosinophilia, thrombocytopenia, leucopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, haemolytic anaemia.
Immune system disorders: Uncommon: angioedema, anaphylaxis.
Nervous system disorders: Common: headache. Uncommon: paraesthesiae. Rare: convulsions.
Gastrointestinal disorders: Common: diarrhoea, vomiting, nausea, abdominal pain. Uncommon: antibiotic-associated colitis.
Hepatobiliary disorders: Common: transaminases increased, blood alkaline phosphatase increased, blood lactate dehydrogenase increased. Uncommon: blood bilirubin increased.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Common: rash, pruritis. Uncommon: urticaria, toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme. Not Known: Drug Reactions with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS Syndrome).
Renal and urinary disorders: Uncommon: blood creatinine increased, blood urea increased
General disorders and administration site conditions: Common: inflammation, pain. Uncommon: thrombophlebitis, pain at the injection site.
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Antibacterials for systemic use, Carbapenems.
Meropenem is a broad-spectrum carbapenem antibiotic. It is active against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Meropenem exerts its action by penetrating bacterial cells readily and interfering with the synthesis of vital cell wall components, which leads to cell death. The bactericidal activity of meropenem results from the inhibition of cell wall synthesis. Meropenem readily penetrates the cell wall of most Grampositive and Gram-negative bacteria to reach penicillin-binding- protein (PBP) targets. Its strongest affinities are toward PBPs 2, 3 and 4 of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa; and PBPs 1, 2 and 4 of Staphylococcus aureus.
Absorption
At the end of a 30-minute intravenous infusion of a single dose in healthy volunteers, mean peak plasma concentrations of meropenem are approximately 23 mcg/mL
Distribution
The average plasma protein binding of meropenem was approximately 2 % and was independent of concentration. After rapid administration (5minutes or less) the pharmacokinetics are biexponential but this is much less evident after 30 minutes infusion.
Metabolism
Meropenem is metabolised by hydrolysis of the beta-lactam ring generating a microbiologically inactive metabolite.
Elimination
Meropenem is primarily excreted unchanged by the kidneys; approximately 70 % (50 –75 %) of the dose is excreted unchanged within 12 hours.
The meropenem injection must not be mixed with other medicinal products.
Chemical and physical in-use stability for a prepared solution for infusion using 0.9% sodium chloride solution has been demonstrated for 6 hours at controlled room temperature (20°C-25°C).
Constituted solution of meropenem in 5% glucose (dextrose) solution should be used immediately, i.e. within 30 minutes following Constitution. Do not freeze the Constituted solution.
Injection: Meropenem to be used for bolus intravenous injection should be constituted with sterile water for injection.
Infusion: For intravenous infusion meropenem vial may be directly constituted with 0.9% sodium chloride or 5% glucose (dextrose) solutions for infusion. Standard aseptic techniques should be used for solution preparation and administration.
Single dose vial.
Pantoprazole injection should not be prepared or mixed with other medicinal preparations.
WhatsApp us
